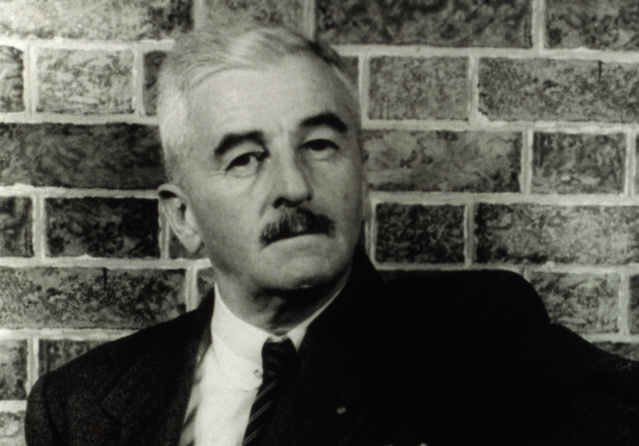
William Faulkner was born in 1897 in New Albany, Mississippi, where his father was then working as a conductor on the railroad built by the novelist’s great-grandfather, Colonel William Falkner (without the “u”), author of The White Rose of Memphis. Soon the family moved to Oxford, thirty-five miles away, where young Faulkner, although he was a voracious reader, failed to earn enough credits to be graduated from the local high school. In 1918 he enlisted as a student flyer in the Royal Canadian Air Force. He spent a little more than a year as a special student at the state university, Ole Miss, and later worked as postmaster at the university station until he was fired for reading on the job.
Encouraged by Sherwood Anderson, he wrote Soldier’s Pay (1926). His first widely read book was Sanctuary (1931), a sensational novel which he says that he wrote for money after his previous books—including Mosquitoes (1927), Sartoris (1929), The Sound and the Fury (1929), and As I Lay Dying (1930)—had failed to earn enough royalties to support a family.
A steady succession of novels followed, most of them related to what has come to be called the Yoknapatawpha saga: Light in August (1932), Pylon (1935), Absalom, Absalom! (1936), The Unvanquished (1938), The Wild Palms (1939), The Hamlet (1940), and Go Down, Moses, and Other Stories (1941). Since World War II his principal works have been Intruder in the Dust (1948), A Fable (1954), and The Town (1957). His Collected Stories received the National Book Award in 1951, as did A Fable in 1955. In 1949 Faulkner was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature.
Recently, though shy and retiring, Faulkner has traveled widely, lecturing for the United States Information Service. This conversation took place in New York City, early in 1956.
INTERVIEWER
Mr. Faulkner, you were saying a while ago that you don’t like interviews.
WILLIAM FAULKNER
The reason I don’t like interviews is that I seem to react violently to personal questions. If the questions are about the work, I try to answer them. When they are about me, I may answer or I may not, but even if I do, if the same question is asked tomorrow, the answer may be different.
INTERVIEWER
How about yourself as a writer?
FAULKNER
If I had not existed, someone else would have written me, Hemingway, Dostoyevsky, all of us. Proof of that is that there are about three candidates for the authorship of Shakespeare’s plays. But what is important is Hamlet and A Midsummer Night’s Dream, not who wrote them, but that somebody did. The artist is of no importance. Only what he creates is important, since there is nothing new to be said. Shakespeare, Balzac, Homer have all written about the same things, and if they had lived one thousand or two thousand years longer, the publishers wouldn’t have needed anyone since.
INTERVIEWER
But even if there seems nothing more to be said, isn’t perhaps the individuality of the writer important?
FAULKNER
Very important to himself. Everybody else should be too busy with the work to care about the individuality.
INTERVIEWER
And your contemporaries?
FAULKNER
All of us failed to match our dream of perfection. So I rate us on the basis of our splendid failure to do the impossible. In my opinion, if I could write all my work again, I am convinced that I would do it better, which is the healthiest condition for an artist. That’s why he keeps on working, trying again; he believes each time that this time he will do it, bring it off. Of course he won’t, which is why this condition is healthy. Once he did it, once he matched the work to the image, the dream, nothing would remain but to cut his throat, jump off the other side of that pinnacle of perfection into suicide. I’m a failed poet. Maybe every novelist wants to write poetry first, finds he can’t, and then tries the short story, which is the most demanding form after poetry. And, failing at that, only then does he take up novel writing.
(…)